AFPM: Will the ‘26-‘27 RFS ‘unleash’ affordable, reliable energy?
That’s looking like a hard no.
The Environmental Protection Agency is attempting to finalize the largest and most expensive Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) mandate in history. This would significantly increase costs for American refiners and consumers.
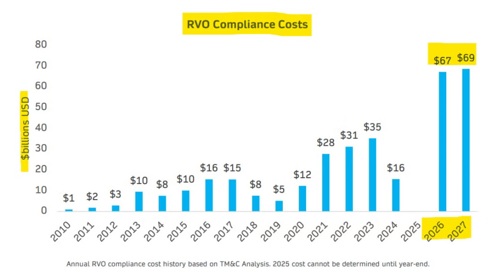
Analysis done this summer by Turner Mason & Co. projects the RFS could cost the American people and American fuel producers nearly $70 billion both years. That’s about twice as expensive as the 2023 RFS, the current annual record-holder.
It’s worth noting that EPA shows a different cost projection in its regulatory impact analysis, and that deserves some explanation.
- Turner Mason calculated the likely cost of all the RFS regulatory credits (known as RINs) refiners would need to turn into EPA in 2026 and 2027 to prove compliance with the RFS mandate. Turner Mason determined those RINs would cost roughly $70 billion both years.
- EPA published a “societal cost” of the RFS program which doesn’t include the cost of any RFS regulatory credits. Even with that huge omission, EPA’s cost v. benefit ratio is still pretty bad: they say the RFS will impose societal costs of $6.7 billion per year, while offering just $200 million in benefits (that means even in the most flattering light, the RFS leaves us $6.5 billion in the red).
- Two additional cost notes:
- EPA’s omission of RFS credit costs is especially frustrating since the agency claims RFS costs are “passed through to consumers in [the form of] higher prices on the gasoline and diesel” obligated refineries produce.
- EPA’s cost estimates could be even further off base if the Agency chooses to reallocate RFS obligations from small refineries granted relief to larger refineries. EPA has left the door open for the possibility of reallocation on top of the 2026-2027 RFS proposal, which would further inflate the cost of the RFS mandate.
- Two additional cost notes:

Why are compliance costs so high, and what can EPA do about it? Glad you asked!
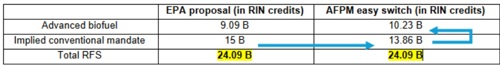
RFS compliance costs are driven by one problem more than any other: the price of regulatory credits for corn starch ethanol are artificially inflated. The price of ethanol credits is driven up by higher priced advanced biofuel credits, and that’s because advanced biofuels must also be used to satisfy a small portion of the RFS implied conventional mandate (that’s part of the RFS where corn ethanol lives). Advanced biofuels are needed to meet the implied conventional mandate because gasoline consumption is trending down in the United States and there’s a limit to how much corn ethanol can be blended into gasoline, based on vehicle and fuel infrastructure compatibility and demand from drivers. Advanced biofuels make up the difference.
EPA can cut RFS compliance costs by more than half, without reducing overall biofuel blending at all. All the agency needs to do is move the small volume of advanced biofuels from the implied conventional category over to the advanced category. This would just make sure the volume tables match what EPA has already recognized elsewhere: that blending 15 billion gallons of corn ethanol isn’t possible in 2026 or 2027. Setting the implied conventional mandate a little lower and raising the advanced mandate by the same amount keeps overall biofuel gallons equal, while cutting the cost of ethanol regulatory credits and the total RFS price tag by more than $35 billion.






Comments