TOYO develops MRF-Z Neo—A compact reactor optimized for small-scale green methanol production
Toyo Engineering Corporation (President and CEO Eiji Hosoi, TOYO) has developed MRF-Z Neo, a new compact methanol synthesis reactor specifically designed for small-scale production of green methanol – namely bio-methanol and eMethanol.
Building on TOYO’s proven large-scale methanol synthesis technology, MRF-Z, this new reactor has been optimized for small-scale plants. It is well-suited for leveraging locally available biomass and renewable energy sources, enabling efficient green methanol production on a regional scale.
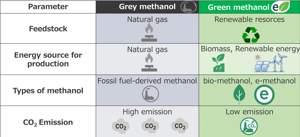
Rising demand for green methanol. As global efforts toward decarbonization gain momentum, green methanol is gaining attention as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuel-derived methanol.
Methanol is a highly versatile chemical used in fuels (marine fuel, jet fuel, gasoline) as well as in a wide range of chemical products (such as resins and adhesives). Transitioning to sustainable production methods using biomass and renewable energy will play a key role in achieving carbon neutrality.
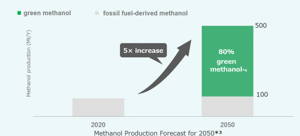
Global methanol demand is projected to grow fivefold by 2050, with approximately 80% expected to come from green methanol. Adoption of green methanol is accelerating, especially in Europe, within the shipping and chemical sectors, making green methanol a promising growth market.
Small-scale plants becoming the mainstream for green methanol production. Green methanol production relies on feedstock like biomass and renewable energy, which are both geographically dispersed and temporally variable. This makes it difficult to sustain stable production using large, centralized plants. Additionally, over 97% of the world’s renewable power plants have a capacity of less than 100 MW, highlighting the growing need for compact reactors that are compatible with decentralized energy sources.
MRF-Z Neo is a next-generation reactor designed specifically for small-scale production. It is based on TOYO’s proven, MRF-Z technology, which has a strong track record in large-scale methanol production plants. MRF-Z Neo inherits several key features of the original large-scale MRF-Z reactor:
- A stepwise cooling structure ensures optimal temperature control throughout the reaction process, improving reaction efficiency while minimizing catalyst consumption.
- A radial gas flow design - from the reactor’s outer shell to its center – ensures low pressure drop and high conversion efficiency.
- Innovative mechanical design, including a unique cooling tube fixation method, delivers long-term operational stability and ease of maintenance.
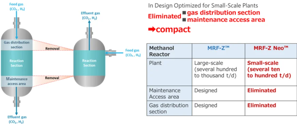
While retaining the advantages of the original MRF-Z, MRF-Z Neo achieves a more compact form by redesigning the maintenance access area and gas distribution section.
By eliminating both the lower maintenance access area and the upper gas distribution section, the reactor’s overall size has been significantly reduced. This compact design leads to lower manufacturing costs, resulting in more cost-effective reactor.
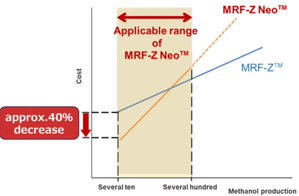
As a result of these improvements, MRF-Z Neo can achieve up to approximately 40% cost reduction compared to a scaled-down version of the conventional MRF-Z reactor.
TOYO’s vision extends beyond the standalone reactor. By combining MRF-Z Neo with its proprietary eMethanol production technology “g-Methanol,” the energy-efficient distillation solution “SUPERHIDIC,” and digital solutions designed to manage fluctuations in renewable energy, TOYO offers a comprehensive solution that enables flexible, cost-efficient and rapid deployment of green methanol production facilities. Through this integrated approach, TOYO aims to accelerate the social implementation of green methanol and contribute to the realization of a carbon-neutral future.






Comments